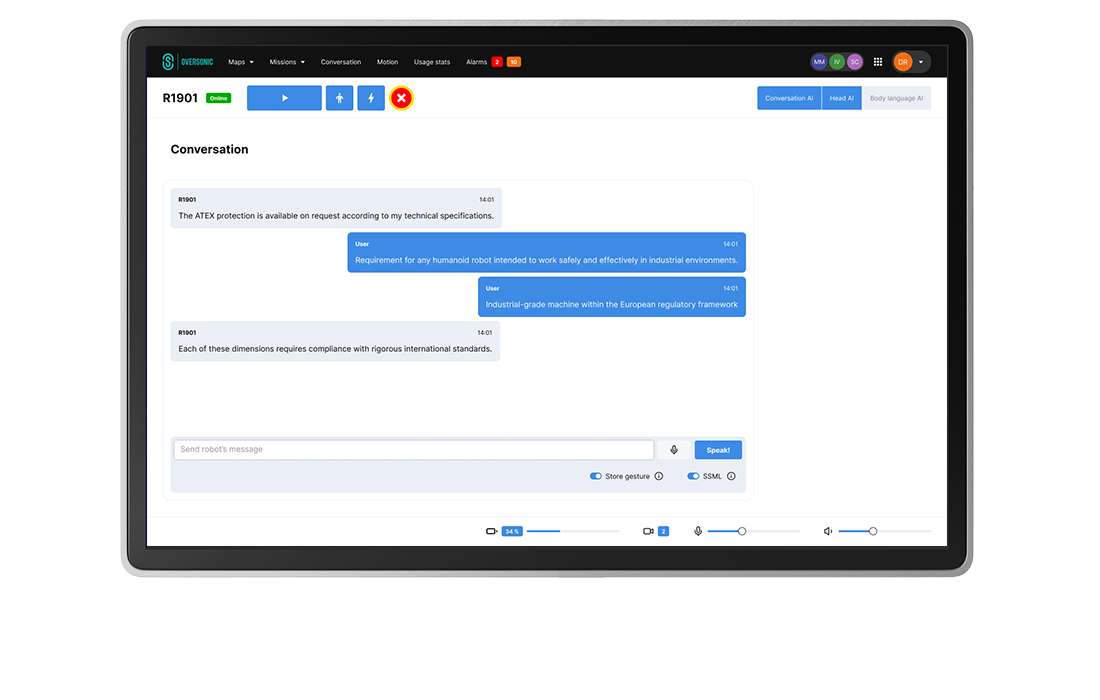
The Conversation Module orchestrates natural, multi-turn voice interactions between humans and robots through an integrated pipeline of audio processing, speech recognition, and AI-driven response generation.
The system manages the complete conversational workflow from microphone input capture to speaker output, coordinating multiple specialized services including transcription, language processing, and audio synthesis.
Built on a modular architecture, it supports configurable AI agents that can be tailored with specific personalities, knowledge bases, and linguistic capabilities.
The module handles both structured command recognition and free-form dialogue, enabling robots to engage in contextual conversations while maintaining the ability to execute specific tasks through voice commands.
| ➔ | Multi-turn conversation flow Supports continuous dialogue sessions where users can engage in extended conversations with contextual awareness and memory retention throughout the interaction. |
|---|---|
| ➔ | Intelligent agent integration Configurable AI agents with customizable personality, knowledge base, LLM models, and voice parameters that determine the robot's conversational behavior and expertise domain. |
| ➔ | Real-time audio processing Integrated audio-service for high-quality voice input capture and output generation with streaming transcription capabilities for responsive interactions. |
| ➔ | Conversation triggers Multiple conversation initiation methods including face detection-based engagement and always-on listening mode for demonstrations and remote interactions. |
| ➔ | Command recognition Support for hooks (webhook-enabled voice commands for external service integration) and triggers (direct voice commands with 100% accuracy for mission execution). |
| Modular agent architecture |
| Connectors for most LLMs (Mistral, Gemini, GPT, others) |
| Multi-language configuration |
| Single utterance mode |
| Always-on Mode |
| Dynamic language switching without interruption |



